Difference between revisions of "Installing MansOS"
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
* What is the '''target platform''' or platforms that you will be developing for. At least you should know what is the main micro controller. MansOS supports several popular target controller families: TI msp430, 8-bit Atmega controllers and Nordic Semiconductor nRF24LE1. One can also compile the application for the current PC host, for example, for simulation and debugging purposes. |
* What is the '''target platform''' or platforms that you will be developing for. At least you should know what is the main micro controller. MansOS supports several popular target controller families: TI msp430, 8-bit Atmega controllers and Nordic Semiconductor nRF24LE1. One can also compile the application for the current PC host, for example, for simulation and debugging purposes. |
||
= Step |
= Step 1: Prerequisites = |
||
In general, the following programs are needed: |
In general, the following programs are needed: |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Linux and *BSD == |
== Linux and *BSD == |
||
As often, you have two options: installing (and compiling) the latest and greatest tools by hand, or have an automated installation of some fairly recent version. |
|||
=== Using manual installation === |
=== Using manual installation === |
||
| Line 59: | Line 61: | ||
=== Installation using RPM packages === |
=== Installation using RPM packages === |
||
You may already have certain compilers and tools installed if you have TinyOS. Or you could install [http://www.tinyos.net/tinyos-2.x/doc/html/install-tinyos.html TinyOS rpm packages]. The RPM packages are available here: |
|||
http://www.tinyos.net/dist-2.0.0/tools/windows/msp430tools-base-0.1-20050607.cygwin.i386.rpm |
http://www.tinyos.net/dist-2.0.0/tools/windows/msp430tools-base-0.1-20050607.cygwin.i386.rpm |
||
http://www.tinyos.net/dist-2.0.0/tools/windows/msp430tools-python-tools-1.0-1.cygwin.noarch.rpm |
http://www.tinyos.net/dist-2.0.0/tools/windows/msp430tools-python-tools-1.0-1.cygwin.noarch.rpm |
||
| Line 75: | Line 77: | ||
The .bashrc file can be found in your home directory, which is a location like this: ''C:\cygwin\home\username\.bashrc''. |
The .bashrc file can be found in your home directory, which is a location like this: ''C:\cygwin\home\username\.bashrc''. |
||
=== Support for serial port interfacing with |
=== Support for serial port interfacing with sensor nodes === |
||
To upload compiled programs to a mote you'll need to install proper USB to serial port drivers first. The drivers are included in Tmote Sky driver CD. If you don't have the CD, download the drivers from [http://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm here]. For more details consult the Tmote Sky Quick Start Guide, section USB Serial COM Driver Install (page 7). The guide is availabe at http://www.cems.uvm.edu/~crobinso/mote/tmote-sky-quickstart-110.pdf. |
To upload compiled programs to a mote you'll need to install proper USB to serial port drivers first. The drivers are included in Tmote Sky driver CD. If you don't have the CD, download the drivers from [http://www.ftdichip.com/Drivers/VCP.htm here]. For more details consult the Tmote Sky Quick Start Guide, section USB Serial COM Driver Install (page 7). The guide is availabe at http://www.cems.uvm.edu/~crobinso/mote/tmote-sky-quickstart-110.pdf. |
||
| Line 91: | Line 93: | ||
... |
... |
||
= Step |
= Step 2: Getting MansOS sources = |
||
MansOS source code is available either using SVN version control or in a pre-packaged form. |
|||
=== Using version control system === |
=== Using version control system === |
||
| Line 107: | Line 110: | ||
If you also want to receive SVN write access, contact MansOS developers. |
If you also want to receive SVN write access, contact MansOS developers. |
||
=== Using package management software (broken |
=== Using package management software (currently broken...) === |
||
Get and install the MansOS Debian package: http://mansos.net/box/mansos-0.1.0_20101101_all.deb |
Get and install the MansOS Debian package: http://mansos.net/box/mansos-0.1.0_20101101_all.deb |
||
| Line 113: | Line 116: | ||
The package depends on either ''msp430-tools'' metapackage, ''tinyos-required-msp430'' package, or ''tinyos-required-avr'' package. |
The package depends on either ''msp430-tools'' metapackage, ''tinyos-required-msp430'' package, or ''tinyos-required-avr'' package. |
||
= Step |
= Step 3: Testing your installation = |
||
$ ls mansos |
$ ls mansos |
||
Revision as of 18:45, 2 November 2010
When you install MansOS development environment you need to know two things:
- What is the development host where you will compile your applications. All of the major desktop operating systems (Linux, Windows, MacOS) are supported as MansOS development hosts.
- What is the target platform or platforms that you will be developing for. At least you should know what is the main micro controller. MansOS supports several popular target controller families: TI msp430, 8-bit Atmega controllers and Nordic Semiconductor nRF24LE1. One can also compile the application for the current PC host, for example, for simulation and debugging purposes.
Step 1: Prerequisites
In general, the following programs are needed:
- Compiler and binutils
- For example, msp430-gcc for TelosB and msp430 platforms or avr-gcc for Atmega platform
- GNU make
- Python
If you already have them, you can skip this section.
Linux and *BSD
As often, you have two options: installing (and compiling) the latest and greatest tools by hand, or have an automated installation of some fairly recent version.
Using manual installation
For MSP430 based platforms, download and install either of these:
- http://mspgcc4.sourceforge.net/ - provides MSP tools based on GCC version 4
- http://mspgcc.sourceforge.net/ - alternative, should you need the older GCC version 3
After installing msp430-gcc you'll need to set up you $PATH correctly. Add this line to your ~/.bashrc file (assuming msp430-gcc is installed in /opt):
export PATH="/opt/msp430-gcc/bin:$PATH"
Using package management software
Install MSP430 tools:
http://mansos.net/deb/binutils-msp430_2.17-2_i386.deb - MSP430 binutils http://mansos.net/deb/gcc-msp430_3.2.3-2_i386.deb - MSP430 GCC compiler http://mansos.net/deb/msp430-libc_20071026_i386.deb - MSP430 libc http://mansos.net/deb/msp430-tools_i386.deb - MSP430 tools metapackage
Alternatively, install the tool packages provided by TinyOS.
Windows
MansOS on Windows is supported using Cygwin. (It may also work with MinGW.)
Download and install Cygwin. Here's a direct link to the setup program.
Make sure to select the following Cygwin packages:
- gcc
- make
- python
- svn
- openssh (required only if you'll want to use non-anonymous SVN access)
- rpm (required only if you'll want to use the pre-made RPM packages for installation)
After this you'll need to install msp430 tools. There are two options for this:
- Installing the tools manually
- Installing the tools from RPM packages provided by TinyOS
Manual installation
Follow the instructions in mspgcc homepages. Download and install either of these:
- http://mspgcc4.sourceforge.net/ - provides MSP tools based on GCC version 4
- http://mspgcc.sourceforge.net/ - same, but for GCC version 3 (older)
Installation using RPM packages
You may already have certain compilers and tools installed if you have TinyOS. Or you could install TinyOS rpm packages. The RPM packages are available here:
http://www.tinyos.net/dist-2.0.0/tools/windows/msp430tools-base-0.1-20050607.cygwin.i386.rpm http://www.tinyos.net/dist-2.0.0/tools/windows/msp430tools-python-tools-1.0-1.cygwin.noarch.rpm http://www.tinyos.net/dist-2.0.0/tools/windows/msp430tools-binutils-2.16-20050607.cygwin.i386.rpm http://www.tinyos.net/dist-2.0.0/tools/windows/msp430tools-gcc-3.2.3-20050607.cygwin.i386.rpm http://www.tinyos.net/dist-2.0.0/tools/windows/msp430tools-libc-20050308cvs-20050608.cygwin.i386.rpm
Install the RPM packages:
$ rpm -ivh --force --nodeps --ignoreos *.rpm
Finishing installation
Set up you $PATH to point to msp430-gcc tools. Add this line to your ~/.bashrc file (assuming msp430-gcc is installed in /opt):
export PATH="/opt/msp430-gcc/bin:$PATH"
The .bashrc file can be found in your home directory, which is a location like this: C:\cygwin\home\username\.bashrc.
Support for serial port interfacing with sensor nodes
To upload compiled programs to a mote you'll need to install proper USB to serial port drivers first. The drivers are included in Tmote Sky driver CD. If you don't have the CD, download the drivers from here. For more details consult the Tmote Sky Quick Start Guide, section USB Serial COM Driver Install (page 7). The guide is availabe at http://www.cems.uvm.edu/~crobinso/mote/tmote-sky-quickstart-110.pdf.
Now install MansOS sources and check that motelist detects all motes attached to the Windows PC:
$ motelist Reference CommPort Description ---------- ---------- ---------------------------------- M4AOQGBQ COM8 tmote sky
MacOS
... TODO ...
Step 2: Getting MansOS sources
MansOS source code is available either using SVN version control or in a pre-packaged form.
Using version control system
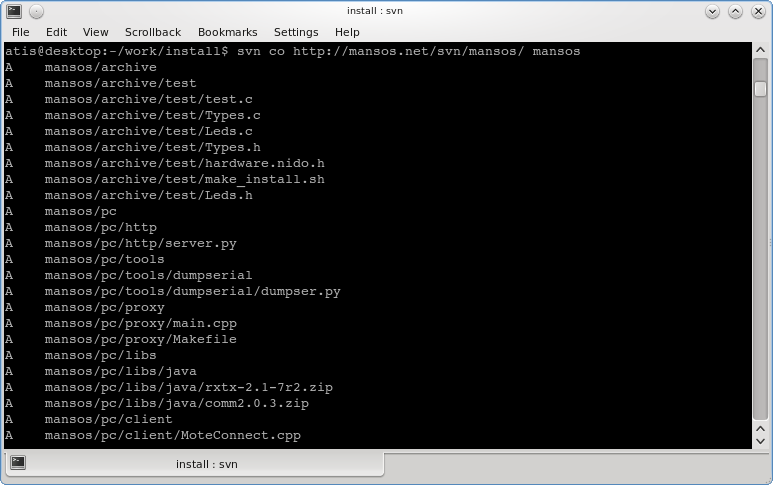
MansOS sources are available for anonymous checkout from SVN:
$ svn co http://mansos.net/svn/mansos/ mansos A mansos/archive A mansos/archive/test ... Checked out revision 732.
If you also want to receive SVN write access, contact MansOS developers.
Using package management software (currently broken...)
Get and install the MansOS Debian package: http://mansos.net/box/mansos-0.1.0_20101101_all.deb
The package depends on either msp430-tools metapackage, tinyos-required-msp430 package, or tinyos-required-avr package.
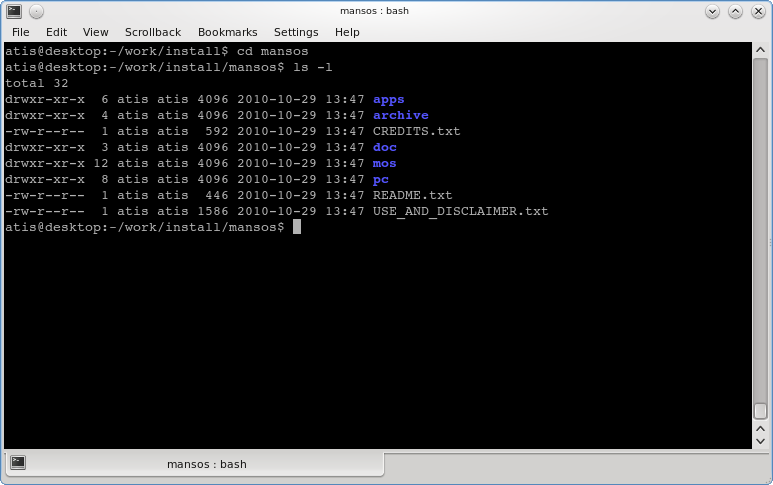
Step 3: Testing your installation
$ ls mansos apps archive CREDITS.txt doc mos pc README.txt USE_AND_DISCLAIMER.txt
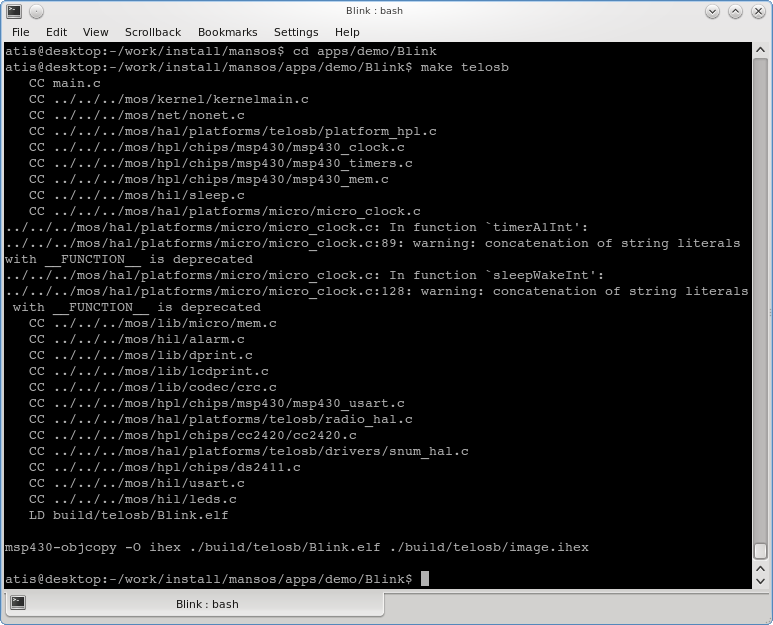
To test building for TelosB (Tmote Sky):
$ cd mansos/apps/demo/Blink $ make telosb
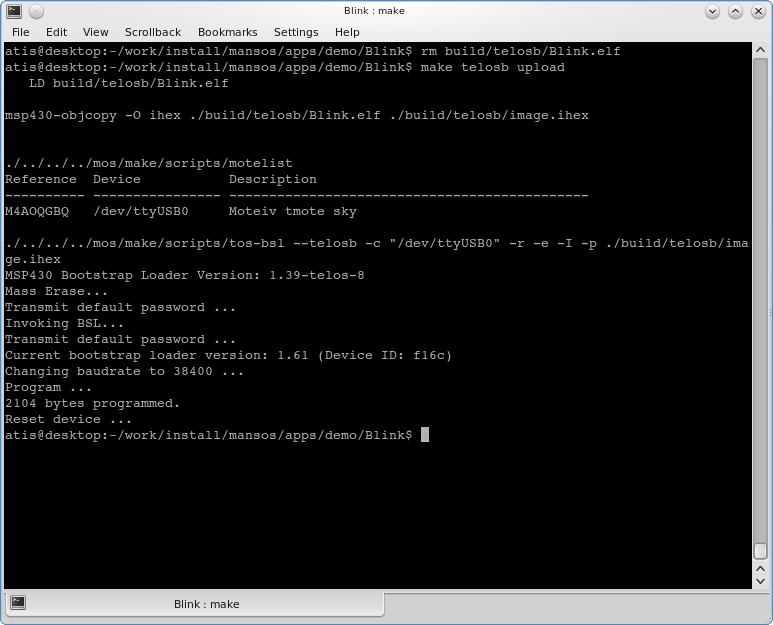
If you have motes attached:
$ make telosb upload
To test serial port output:
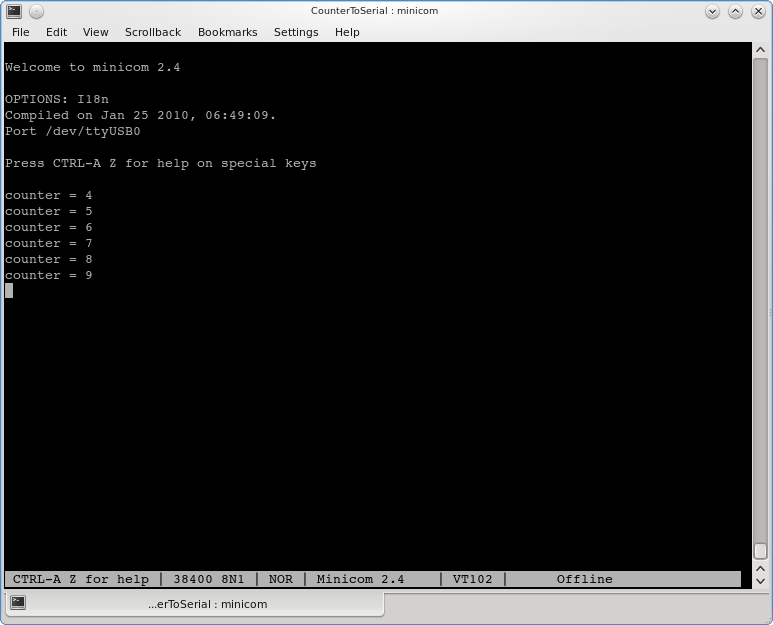
$ cd mansos/apps/demo/CounterToSerial $ make telosb upload
Now you can use a tool like minicom or putty (on Windows) to monitor the serial port. The settings: baudrate=38400, flow-control turned off.
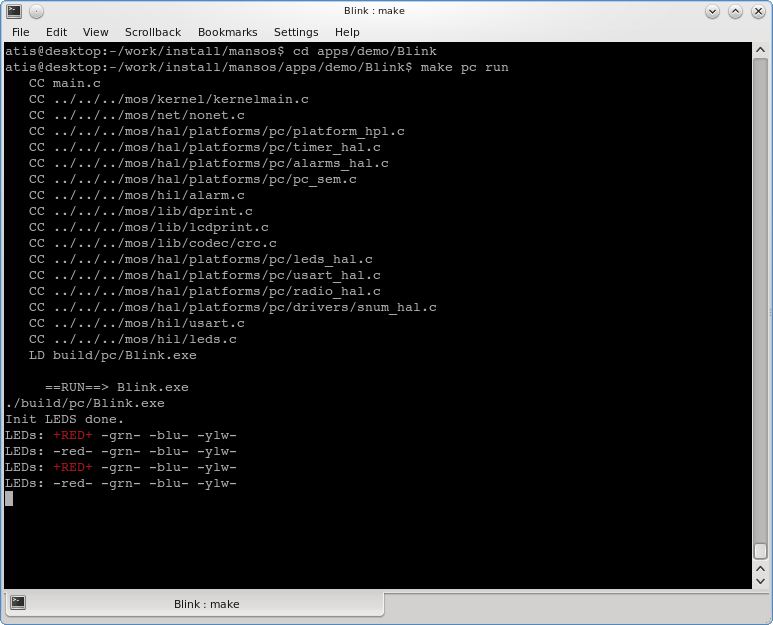
To test the PC simulator:
$ make pc $ make pc run